
National selection of top producer of
poison and fertilizer
in Iran

Omid International Conference
International Conferences Center
In Tehran

Omid Second International Conference
International Conferences Center
In Iran

Omid Third International Conference
International Conferences Center
In Iran

Omid Fourth International Exhibition
International Conferences Center
In Tehran

11th International Agricultural Industry
Exhibition
Machinery and related services

Second Specialized Agricultural Exhibition
The permanent location of
the Bustan fairs

11th International Agricultural Fair
Premier Booth
In Iran

Sixth specialized exhibition
Tehran Agricultural Agencies
In Iran

National Award for Top
Manufacturing Unit
In Iran-gazvin

First place
Safir Cup Tournament
In Winter

Top Team
Ramezan Cup Tournament
TehraniMoghadam

Third place
Safir First Futsal Cup Tournament
itcup

Additives(Adjuvants)
Additives(Adjuvants)
Adjuvant is an additive in a pesticide that, when added to a spray solution, improves the physical properties or modifies and increases the biological activity of the pesticide. Like additives in medicine, these substances themselves have no role in controlling or killing pests. Instead, improves the spray properties, the permeability of pesticides and their ability to kill target organisms and prevent them from being wasted. Additives vary in mode of action, may be multi-functional and are divided into different groups. Additives may have more than one action. A significant number of additives are compounds that differ in chemical structure and function and in this sense, their performance is multiplied. A practical example of a multifunctional additive is a mixture of ammonium sulfate and a polymer. Secondly, a chemical compound or a type of compound may interact at different stages of targeting a pesticide. For example, a polyethylene amine surfactant improves both leaf wetting and glyphosate solution uptake. A distinction can be made between additive functions that have a direct impact on the availability and availability of the active ingredient. Common types of additives used include surfactants, emulsifiers, oils and salts. All of these materials and other compounds modify the spray solution to improve properties such as diffusion, penetration, droplet size or other properties.
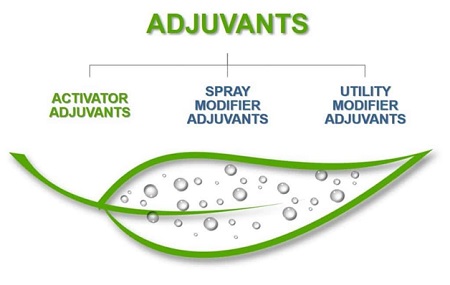
Adjuvants generally consist of two main groups:
The group used in the pesticide formulation is called Built-in (Internal), In – can adjuvant or activator adjuvant and the group that is added separately to the tanker during spraying is called External adjuvant or modifier adjuvant. External adjuvants are divided into two categories: Utility adjuvants and Modifier Adjuvants.
Adjuvants change foliar application conditions to improve the use and effectiveness of conventional pesticides. For pesticides, adjuvants are used to optimize the contact of pesticide with the surface of leaves, soil or insects and reduce drought, protect it from UV damage, increase shelf life, increase solubility or suspend in water. Additives give the pesticide a more stable performance and may be neutralized during operation under certain conditions.
Additives that increase product performance and are considered as Activator adjuvants are consisting of:
- Water’s spreaders
They increase the wetting property or dispersion of toxin droplets on the target surface by reducing the surface tension of the pesticide formulation and improving the dispersion on the target surface (types of surfactants) which are themselves divided into ionic and non-ionic surfactants.
Non –ionic surfactants
They are mostly used in pesticides and bio-pesticides, are compatible with most pesticides and are usually used with systemic pesticides.
Anionic surfactants
They are commonly used to improve the performance of contact insecticides to control relatively immobile pests such as mites, thrips and aphids.
Cationic surfactants
Cationic surfactants are rarely used due to the potential risks of chemical toxicity
Organosilicons
Organosilicons are silicone-based surfactants that have excellent dispensability. These diffusers can facilitate the movement of pesticides on plants and cover and penetrate areas that are not easily accessible. But with all these descriptions, the evaporation rate of the droplets in these surfactants is high.

Shape description:
Shape description: pesticide droplets without adjuvant (top left) and with wetting adjuvant (top right). In the absence of adjuvant, the drops sprayed on the leaf can be seen as a pearl, which results in the lack of proper contact of the pesticide on the leaf (bottom left). By adding a diffuser surfactant, the sprayed droplets spread completely on the leaf.
- Stickers
They increase the adhesion of the drop to the target surface (terpenes and pinols) and thus reduce the Drift of the pesticide from the main path.
- Penetrants
They cause the transfer of the active substance from the target surface to the internal tissue (mineral oils).
Penetrants are generally used to optimize the uptake of active ingredients on broadleaf weeds that are thick in the cuticle, especially in plants that grow in hot and dry conditions. They are much more effective in counteracting dryness by having a strong cuticular tissue. By penetrating into plant cells and intracellular or extracellular transfer, they play an important role in the transfer of chemicals in the form of apoplastic (extracellular), symplastic (intracellular) or translaminar (From leaf surface to below leaf).
Interpretation of shape:
Passage of the active ingredient through apoplastic (extracellular), symplastic (intracellular) and translaminar (from the upper to the lower surface of the leaf).
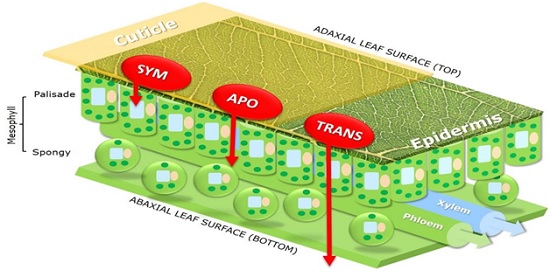
Crop oil concentrates obtained from the combination of vegetable base oil with surfactants act as penetrants (by softening or dissolving the wax layer of the leaf cuticle and facilitating the absorption of the active substance into the leaf) and increase the facilitation of movement in the cell wall and membrane.
- Extenders
Increases the shelf life of the active ingredient by increasing resistance to environmental conditions (ammonium sulfate).
- Humectants
They increase the drying time of the pesticide solution on the target surface (Propylene Glycol).
Modifier Adjuvants
There are additives that change the physical properties of the solution used in spraying and facilitate spraying and increase the safety of its use. These additives include stickers and drift retardants such as thickeners and moisturizers.
Stickers are substances that increase the adhesion of droplets or particles to the surface of the leaf and prevent the active ingredient from being washed away during rain or irrigation. They are often combined with moisturizing or spreading agents to improve the coating.
Utility Adjuvants
There are additives that make it easy to use and include adjuvants that change the way you use them.
- Acidifying/ Buffering agents
Includes modifiers used in conjunction with chemical pesticides, including buffers to maintain and regulate pH in chemical pesticide solutions, thereby reducing the decomposition of pesticides by hydrolysis, such as Phytomax water pH reducer.
- Water Conditioners
Prevents the reaction of hard water ions in the toxic solution and stops the formation of salt and sediment, such as ammonium sulfate and Phytomax water PH reducer.
- Anti-foaming agents
They reduce or stop the formation of foam in the spray tank such as Metopoly siloxane
- Drift reducing agents
They cause a change in the viscosity of the toxic solution, resulting in the formation of larger droplets and an increase in concentration) Polyacrylamides)
- Compatibility agents
They make it possible to mix different agrochemicals by preventing the occurrence of antagonistic effects between them (Ammonium Sulfate).
Adjuvants of AlborzBehSam Co.:
This product has the property of wetting and dispersing and eliminating the surface adsorption forces of water droplets, causing a better and more effective effect of pesticides. Consumption of this product increases the durability and efficiency of toxins, rapid absorption of nutrients and better distribution of toxic solutions and liquid fertilizers.

Consumption of this product increases the efficiency of the pesticides and facilitates its penetration, and also maximizes the dispersion of pesticides and fertilizers in the leaves.

-Modifier of using water spray by regulating the acidity of water
-Stabilizing the formulation of various fertilizer and pesticide solutions
-Prevent the inactivation of pesticides in heavy water
-Significant increase in foliar application due to the presence of soluble nitrogen and phosphorus
-Increase the dispensability of the solution on the leaf
-Improve the performance of a variety of fungicides, insecticides, herbicides and fertilizers
